As per Wikipedia, Dementia is a broad category of brain diseases that cause a long-term and often a gradual decrease in the ability to think and remember that is so severe to the extent of affecting a personÔÇÖs daily functioning. AlzheimerÔÇÖs is the most common type of dementia affecting 60%-70% of the cases.
According to a survey, someone in the world develops dementia every 3 seconds. There were an estimated 50 million people living with dementia in 2017.┬á This number is expected to reach 75 million by 2030! AlzheimerÔÇÖs is a global disease demanding a global framework for action on it.
As per World Health Organisation (WHO), Dementia affects memory, thinking, orientation, comprehension, calculation, learning capacity, language, and judgement.
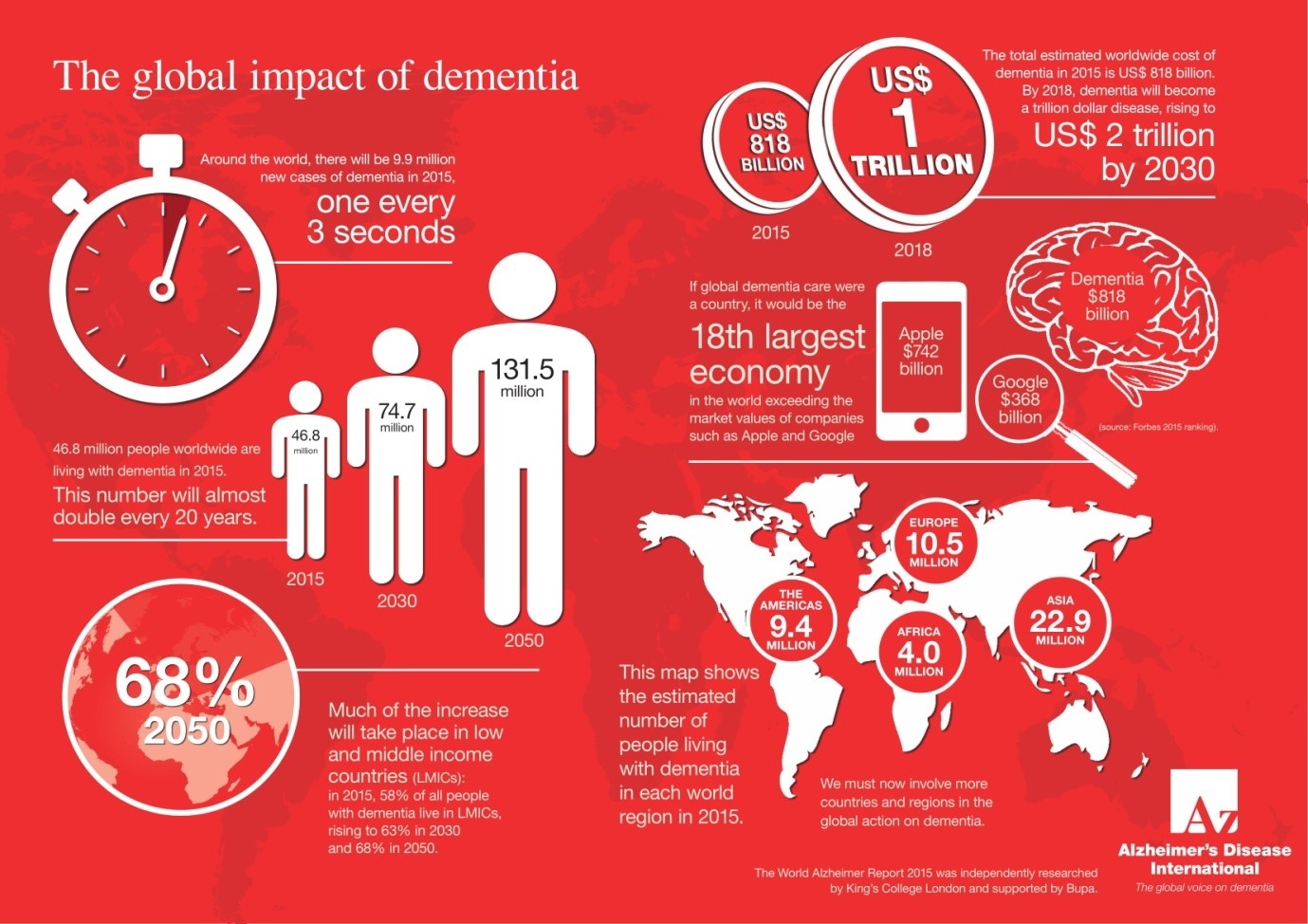
The above infographic shows the global impact of Dementia worldwide. Read on to learn more about AlzheimerÔÇÖs disease.
The Three Stages of Dementia
If your loved one is going through Dementia, then to give the proper care you should know about the stages of Dementia. Knowing them will help you provide the best suitable care to the patient.
Early stage
This stage of Dementia is often overlooked because the onset is gradual. Symptoms are:
- Forgetfulness
- Losing track of time
- Becoming lost in familiar places.
Middle Stage
As the person moves from the early stage to the middle stage, symptoms become clearer. These include:
- Forgetting recent events and peopleÔÇÖs names.
- Increasing difficulty with communication.
- Experiencing behaviour changes including wandering.
 Late stage
In this stage, memory disturbances become more serious and symptoms become obvious. These include:
- Becoming unaware of time and place.
- Facing difficulty while recognizing friends and relatives.
- Having an increasing need for assisted self-care.
- Having difficulty walking.
- Behaviour changes that may escalate including aggression.
Forms of Dementia
AlzheimerÔÇÖs disease is by far the most common & well-known type of Dementia. It affects 60%-70% of the cases. This is heavily researched and various treatments have been investigated.
Vascular Dementia is another kind of Dementia which is also known as ÔÇ£multi-infarct DementiaÔÇØ. It is the second most common form of Dementia.
The third most common form of Dementia is Lewy Body Dementia. It is generally caused by improper proteins that appear in nerve cells and impair functioning.
Frontotemporal Dementia is the fourth most common type of Dementia but it is fairly rare. Memory is preserved but it causes behavioural changes.
Other forms of Dementia that cause cognitive impairment are ParkinsonÔÇÖs disease, HuntingtonÔÇÖs disease, and Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease.
Causes of AlzheimerÔÇÖs disease
It is still unknown what actually causes the deterioration of brain cells but there are some known factors that are known to trigger the development of AlzheimerÔÇÖs disease. These are described below:
Ageing
Ageing is the greatest factor in the development of AlzheimerÔÇÖs disease. The risk of dementia grows after the age of 65 years although symptoms before the age of 65 account for up to 9% of the cases.
Family history
AlzheimerÔÇÖs disease can also be inherited if there is a history of the disease in the family. Genes also play a role in the development of Dementia since they are passed down from generation to generation.
Down syndrome
People with Down syndrome have an extra copy of chromosome 21 which contains protein believed to contribute to the development of AlzheimerÔÇÖs disease. So, people with Down syndrome are at higher risk of it.
Lifestyle factors
There are certain lifestyle factors that can increase the risk of AlzheimerÔÇÖs disease. Some of them are:
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Being physically and mentally inactive.
Prevention and cure
Improving your lifestyle can greatly reduce the risk of AlzheimerÔÇÖs disease. You can do the following things.
Exercise
Regular exercise has been found to greatly reduce the risk of this disease. You should do exercise for 30 minutes at least 3 days per week.
Having a proper diet
Eating fresh vegetables, fruits; whole grains; fish can keep you in a better health state. Also, avoid eating junk food.
Get enough sleep
Evidence suggests that having a better and improved sleep can help prevent AlzheimerÔÇÖs. You should sleep for at least 7-8 hours per night.
Improve brain activity
Being inactive mentally also increases the risk of AlzheimerÔÇÖs. Always keep your brain in the active state and push it to think vigorously by learning new things. Also, connect socially. A greater social contact helps prevent AlzheimerÔÇÖs.
It all depends on our lifestyle. So, lead a better and healthy life. Take care!

